Different storage techniques are suitable depending on the nature of the stored goods and the frequency of use. Different techniques can also be used within the same building.
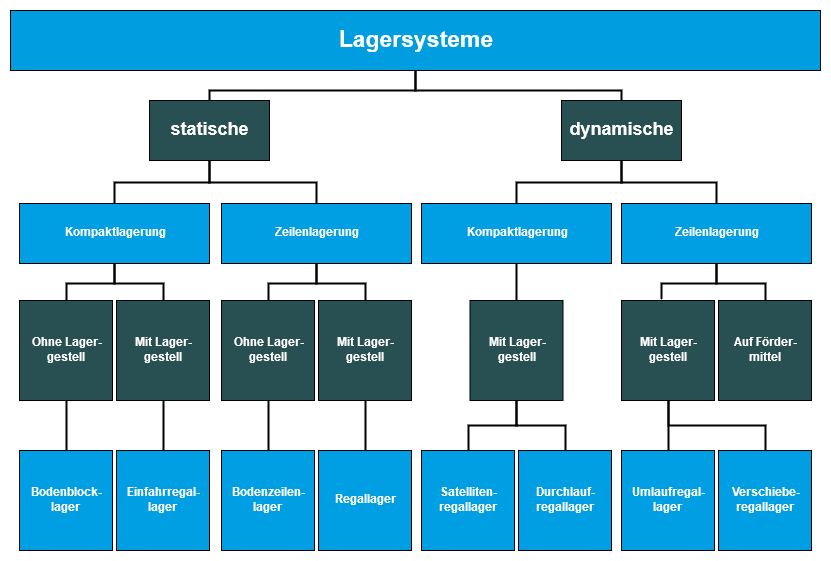
Overview of dynamic and static storage systems in intralogistics.
Storage techniques can be divided into the following types, all of which are listed on this page:
Storage techniques – floor storage
In floor storage, goods are stored without fixed devices such as shelves installed in the warehouse.
Floor storage can be divided into three main types:
- Unstacked storage
- Block storage
- Row storage
Unstacked storage
In unstacked storage, the loading units are stored next to each other. Unstacked storage takes up a lot of space and is therefore less common in closed buildings. It is usually found in open-air warehouses with a small number of different items.
Block storage
In block storage, the loading units are stored without fixed fixtures such as shelves. The goods are usually stacked in several layers on top of and next to each other.
The goods are usually stacked in several layers on top of and next to each other, for example in boxes or on pallets. Block storage is suitable for goods of the same type, goods that are rarely needed, and for high withdrawal quantities.
If the goods are stable and not pressure-sensitive, simple pallets without their own fixtures are sufficient for block storage. Box pallets or crates are suitable for unstable goods.
Advantages and disadvantages of block storage
The advantage of block storage is the cost savings, as the packaging materials are stacked on top of each other and no shelves are required. The absence of shelves also eliminates maintenance and investment costs. Since block storage does not contain shelves that provide a fixed structure for the arrangement of packaging materials, the arrangement of the inventory can be changed at any time.
Disadvantages of block storage include poor access to individual items. In addition, access times can be long when goods need to be removed that are difficult to reach due to other goods stacked in front of them. If sufficient space is available, the goods can be removed or added to the block storage from all sides. However, if access to the warehouse is restricted, the disadvantage is that only the LIFO principle (last in, first out) can be applied without any problems.
Row storage
In row storage, storage is generally the same as in block storage, but there is space between the individual blocks. This allows access to the inventory without having to move units.
In floor row storage, the loading units are placed in rows with the appropriate space between the individual blocks.
This makes it easier to access individual loading units than in block storage.
Advantages and disadvantages of row storage
Advantage of row storage, similar to block storage, is the cost savings, as no shelves are required. This means that the arrangement of the inventory can be changed at any time, as there are no structural elements.
The disadvantage of row storage, as with block storage, is that only the LIFO principle (last in, first out) can be applied without any problems. Row storage also requires more space than block storage.
Storage techniques – static rack storage
In contrast to block and row storage, static rack storage uses fixed racks. Loading units are stored on these racks in single or multiple depths and are only moved again during the removal process.

Shelf storage – © Christian Schwier – Fotolia
Static rack storage can be divided into seven basic types:
- Rack storage with single-depth loading
- Drive-in and drive-through rack storage
- Satellite rack storage
- Shelf rack storage
- Drawer rack storage
- Cantilever rack storage
- Honeycomb rack storage
Rack storage with single-depth loading
One design of the single-depth rack storage system is the classic pallet rack storage. The storage racks consist of fixed field widths between the supports. The fields offer space for one or more pallets, with the load units being stored in a single depth.
The standard bay widths of 2.70 m or 3.60 m are tailored to the dimensions of the Europool pallet (800 mm × 1200 mm) or the German industrial pallet (1000 mm × 1200 mm). The rack structure is usually made of steel or aluminum profiles. Single-deck racking can reach heights of up to forty meters (high-bay warehouses); each individual load unit can be accessed directly.

Shelf storage with single-depth allocation
Advantages and disadvantages of rack storage with single-depth loading
Advantage of single-depth loading is that this type of storage is well suited for automation due to direct access and the geometrically well-defined position of the load unit in the rack compartment.
The disadvantage is the comparatively low volume utilization, as sufficient space must be left between the rack levels and compartments to ensure easy storage and retrieval.
The container rack warehouse as a variant for more sensitive inventory
Another design of the single-depth rack warehouse is the container rack warehouse. The packed inventory generally withstands the horizontal acceleration force better than palletized inventory, as it is enclosed by crates, mesh boxes, or similar containers. Container rack warehouses are often used in automated small parts warehouses (AKL).
Drive-in and drive-through rack warehouses
The drive-in or drive-through rack is a support structure made of profile elements. The industrial truck can drive in or through for storage and retrieval. While drive-in racks use the LIFO principle (last in, first out) for retrieval, the retrieval sequence can vary with drive-through racks. The storage sequence is the same for both rack systems.

Drive-in and drive-through rack with bidirectional conveyor
Continuous cross beams connect the vertical supports and are used to place load units on them. The cross beams are filled from the rear to the front in drive-in and drive-through racks. The load must be raised to the height of the rack level before being driven in. While storage begins on the top level and ends on the bottom level, retrieval takes place in reverse order. This means that the first load unit is placed at the very back of the top level, the second in the level below and also at the very back. Once the bottom level has been reached, storage continues on the top level.
Drive-in racks are racks that can only be accessed from one side. Drive-in racks are secured at the end with stabilizing cross braces. A storage depth of eight load units per storage compartment is considered appropriate. The drive-through rack can be accessed from both sides. Steel superstructures above the top level stabilize the support structure.
Advantages and disadvantages of drive-in and drive-through racking
Advantage of drive-in and drive-through racking is that it combines the advantages of block stacking and rack storage. It is mainly suitable for pressure-sensitive goods. The achievable space utilization is very high.
The disadvantage is that, due to sequential storage, this type of storage is only suitable for items with large quantities per type and a relatively long storage time.
Satellite rack storage
The satellite rack storage system has storage channels in which the load units are stored in multiple depths. Goods are retrieved according to the LIFO principle. The storage channels are accessed by a rail-guided rack conveyor. It is firmly anchored in its storage aisle. Instead of a telescopic fork, a so-called satellite is installed in the rack conveyor. The satellite vehicle is an autonomous vehicle with a very low overall height.

Satellite rack warehouse – © maxoido – Fotolia
Once it has reached the x/z coordinates of the storage compartment, the vehicle detaches itself from the rack conveyor and moves into the storage compartment. It is equipped with a lifting device and can load and unload the load units independently. The cross beams of the rack storage system have two horizontal surfaces: The upper surface is the support surface for the load unit and the lower surface is used as a running surface for the satellite vehicle.
Advantages and disadvantages of satellite rack storage
Advantages of satellite rack storage include compact, space-saving storage, automation and direct access. It thus combines the advantages of drive-in rack storage and single-level rack storage.
The disadvantage is that the steel construction of the rack compartments is very cost-intensive, as the satellite vehicle requires a very high level of workmanship.
Shelf racking
Shelf racking is used to store non-palletized load units. This type of storage is preferred for picking small parts. The stored goods are arranged side by side in containers of different sizes. All stored items can be accessed directly. Fixed or movable partitions are used to divide the rack compartments.

Shelving rack warehouse – © Peter Heckmeier – Fotolia
The dimensions of the compartment shelves depend on the following aspects:
- Quantity to be stored per storage compartment
- Turnover frequency per item
- Range width
- Space availability
- Dimensions of the storage unit
The compartment shelf racks are usually operated manually at a maximum rack height of 2 meters. For ergonomic reasons, the compartments in the upper and lower rows should not be filled with A items (fast-moving items), as the reaching positions are very awkward. For taller racks, mobile ladders or rack servicing devices are used. To make better use of the floor space, shelving racks are often built with multiple levels. Grating is installed between the floors so that warehouse staff can move around.
Advantages and disadvantages of shelving racks
The advantage of this type of storage is its suitability for high throughput rates. Compared to many automated storage systems, it is very easy to respond to highly fluctuating daily traffic patterns. Shelf racking is also extremely reliable and functionally secure. The necessary investment is moderate.
The disadvantage of this type of storage is its limited potential for automation. The personnel requirements are correspondingly high.
Drawer racking
Drawer racking is used to achieve clear and space-saving storage. Loading units are stored in drawers. The design is similar to a conventional drawer cabinet. It is often used in combination with a shelf rack.
Advantages and disadvantages of drawer rack storage
Advantages are, as with shelf racks, low susceptibility to faults, functional reliability and suitability for high throughput rates.
Disadvantages include high personnel requirements and, compared to shelving racks, less flexibility in the compartment division of the drawers.
Cantilever racks
Cantilever racks are suitable for the proper storage of long goods, such as bar stock and stacks of panels. They are primarily used in the iron and wood processing industries.
The storage rack consists of vertically arranged center supports with stand feet. The cantilever arms are side arms on which the stored goods are placed. The length of the cantilever arms and the distance between the center supports depend on the load to be carried. The cantilever arms are attached to the central supports by means of welded, screwed or hook connections. Whether extendable telescopes or cantilever arms with roll-off protection for bar stock are used, for example, depends on the area of application. Storage and retrieval takes place transversely to the rack and is usually carried out manually with a crane or forklift truck.
Advantages and disadvantages of cantilever rack storage
Advantages include individual access to stored goods, compact and proper storage of special goods, and good visibility.
Disadvantages include the large amount of space required for operation and limited automation options. In addition, the investment costs are very high.
Honeycomb rack
The honeycomb rack is only suitable for storing long goods. Many designs require the use of long goods pallets or cassettes to secure the bar stock. The containers are inserted into rack compartments at the front, giving the rack wall a honeycomb appearance when viewed from the front. Special load handling devices are used to store and retrieve the long goods cassettes from the rack conveyors. To enable the heavy long goods cassettes to be pushed into the compartment with minimal friction, the rack compartments are often equipped with roller conveyors or similar devices.

Honeycomb rack storage – Image source: © Toa555 – Fotolia.com
Advantages and disadvantages of honeycomb racking
Advantage of this type of storage is its suitability for automation. Honeycomb racking is mainly used for space-saving storage of slow-moving items.
Disadvantage is that the use of rack conveyors limits the handling capacity of this type of racking.
Storage techniques – Dynamic rack storage
Storage equipment is considered dynamic if the load units are moved on the rack after being stored. A distinction is made between the movement of load units on fixed racks, the movement of load units with moving racks, and the movement of load units with conveyor equipment.

Front view of a dynamic shelving system – © timstieffenhofer – Fotolia
Dynamic rack storage can be divided into six basic types:
- Flow rack storage
- Compact rack storage
- Shift rack storage
- Push-in rack storage
- Circulating rack storage
- Rotary rack
Flow rack storage
In flow rack storage, the stored goods move continuously from the storage side to the retrieval side in a rack channel. The rack channels are arranged in blocks. Only one type of item is stored per rack channel.
The load units are moved either by the force of gravity acting on the rack or by external influences, such as a powered roller conveyor. In the case of movement by gravity, the track is inclined by two to eight degrees. The inclination of the track can be readjusted at any time using plug connections. This is necessary if the load units on the track no longer move by themselves.
To facilitate access, in a container flow rack, the track is inclined so that the front load unit is at an angle of up to thirty degrees to the load unit behind it. The channel length should not exceed twenty meters.
Pallet flow racks, on the other hand, are loaded and unloaded with the aid of forklift trucks. Access is relatively easy, as the angle of inclination of the fork can be adjusted to match the inclination of the rack channel. The channel is usually up to forty meters long.
Advantages and disadvantages of flow rack storage
Advantages of flow rack storage include its good, fixed structure, clarity, and automation. It enables high throughput rates.
Disadvantages include the fact that although channels can be easily attached to rows of racks, restructuring the rack channels to accommodate a changed product range during operation is only possible to a limited extent. Depending on the materials handling technology, the investment costs and susceptibility to faults are relatively high.
Compact rack storage
A compact rack storage system is highly dynamic and usually consists of many autonomous units. Loading units are stored on roll pallets and connected by couplings. Several units are joined together in this way.

View of a compact rack warehouse © Christophe Fouquin ‒ Fotolia.com
Transfer carts, also known as pallet trolleys, are used for storing and retrieving pallets or for coupling and uncoupling them. When a trolley is coupled, the attached pallets are moved along with it when the front pallet is pulled. Lifting and lowering stations serve as transport conveyors on a vertical level. Buffer spaces are used to sort loading units so that they can be made available as quickly as possible.
Advantages and disadvantages of compact rack storage
Advantage of compact storage is that several trolleys and lifting/lowering stations can be used simultaneously on each level. This allows a high overall throughput to be achieved. In addition, the warehouse can be expanded in a modular fashion.
The disadvantage is the high investment required to enable automation.
Shuttle rack storage
In shuttle rack storage, the load units are stored in rows. The storage racks are mounted on undercarriages, which in turn are located on guide rails. This allows the racks to be moved horizontally on the rails.
The individually driven undercarriages usually accommodate a double rack, i.e., two rows of racks. Double racks are usually placed next to each other. Before a specific storage compartment can be accessed, adjacent rows of racks must be moved to form an aisle.
Only when the space between the rows is wide enough can the conveyor vehicle enter the aisle. Depending on the specific requirements, a mobile rack system can be used, for example, for pallet or cantilever racks.
Advantages and disadvantages of a mobile rack warehouse
A major advantage of mobile racks is that they allow maximum utilization of space. In addition, the stored goods are protected from external influences within a assembled block. The flexible design of the individual aisles between the racks is also worth mentioning.
Disadvantages include the higher investment costs and the time required for each rack movement until the racks have been moved to the appropriate removal position.
Push-back rack
The push-back rack consists of several double racks arranged one behind the other. Its design is similar to that of the flow rack. However, in the push-back rack, the inventory is stored and retrieved from the same side.

A shelf rack storage system
Rollers are attached to the underside of the shelves so that inventory can be removed from the individual compartments. This allows each shelf to be pulled out individually. If large containers or pallets are to be stored in the push-in rack, they are removed using industrial trucks. In this case, no rollers are attached to the shelf. Light-duty racks are guided by guide rails.
Advantages and disadvantages of push-back racking
The advantage of push-back racking is that it makes similar good use of space as mobile racking.
The disadvantage is the low turnover rate. Due to the inventory being stored one behind the other, only the LIFO principle (“last in, first out”) is possible without any problems.
Additional investment is required for push-back racking with roller bases.
Carousel racking
Carousel racking is a dynamic racking system in which the storage units are moved by a rotary movement of the entire storage rack.
The “goods-to-person” picking principle applies, i.e., the picker is at a workstation and the storage rack rotates until the desired storage compartment is available. While the operator removes goods from one rack, the next position to be targeted can already be searched for in the adjacent rack. Short access times can be achieved by controlling the rack rotation using optimized compartment preselection.
Depending on the direction of rotation, two types of racks can be distinguished:
- Carousel rack storage
- Paternoster rack storage
In carousel rack storage, the storage rack is moved horizontally. Gondolas are suspended from driven chains. These gondolas are in turn divided into individual storage compartments.
In paternoster rack storage, the storage rack is moved vertically. It is mostly used for storing small parts.
Advantages and disadvantages of carousel rack storage
Advantages of carousel rack storage include short access times and high throughput rates.
Disadvantages include the impact of the high degree of mechanization on flexibility. The adaptability to a changed product range structure is very low. The flow rack is therefore unsuitable for rush orders. For this reason, the flow rack is preferred for continuous order intake.
Rotary rack
A rotary rack is a sorting storage system for small containers. It is highly dynamic and combines the principles of the two storage types “carousel” and “paternoster” used in flow racks.
The containers are stored on several levels above each other. These levels rotate independently of each other around an axis. This horizontal principle is combined with a vertically circulating paternoster. In each storage and retrieval cycle, the paternoster and at least one level move.
Advantages and disadvantages of rotary racks
Advantages of rotary racks include high retrieval throughputs, as order items are distributed evenly across all levels and can be accessed in parallel.
Disadvantage is that maintenance costs are relatively high due to the high degree of automation.
Storage techniques – storage on conveyors
In materials handling technology, the term “conveyors” refers to devices and aids used for transporting goods. Aids can be, for example, cartons, boxes, pallets, and mesh boxes. The storage of inventory directly on the conveyor system is used when the functions of “conveying” and “storage” are to be combined. The integration of these basic logistics functions is sought, for example, in parcel sorting systems. Classic warehouses use continuous material handling systems and discontinuous material handling systems mainly for transporting inventory.
For storage on conveyor systems, there is the option of storage on continuous material handling systems and storage on discrete material handling systems.
Examples of storage on continuous material handling systems include:
- Roller conveyors
- Belt conveyors
- Circular conveyors (e.g. Paternoster)
- Chain conveyors
Examples of storage on discrete material handling systems include:
- Motor vehicles (e.g., forklifts)
- electric overhead monorail systems
- automatic vehicles
- storage and retrieval machines
Storage of hanging goods
Hanging goods are stored goods that may only be transported or stored in a hanging position, such as textiles or certain foods. These special goods may only be stored in this way, as otherwise damage or loss of quality may occur.

Storage of hanging goods
The simplest solution: The warehouse does not consist of storage spaces for pallets and packages, but offers static hanging racks. If only storage spaces are available in the warehouse, the inventory is hung on trolleys. Trolleys are defined as loading units, similar to pallets. They usually consist of a tall trolley on casters, in which the inventory can be hung using one or more rods. A trolley has a certain load capacity and can then be stored using the usual methods. Each trolley should contain one type of inventory (for example, the same item in the same size) so that you don’t have to search for different items within the actual storage unit. This saves time, is less prone to errors, and provides a better overview of available storage capacity. The trolleys are then booked into a fixed storage location.
Automated storage of hanging goods
The methods described above for storing hanging goods properly usually apply to companies whose warehouses are not exclusively designed for hanging goods or who do not want to make major changes to their existing storage facilities. If a warehouse is designed specifically for hanging goods, an automated high-bay warehouse is often used. The inventory hangs on mobile storage rods, which can then be coordinated fully automatically to the respective storage locations or transfer stations. A pure high-bay warehouse for hanging goods has significantly lower investment and personnel costs than a classic high-bay warehouse with storage locations.
Special case: channel rack warehouse
A channel rack warehouse consists of several through-running tracks or insertion channels that are arranged next to and above each other in a honeycomb pattern.
Different storage techniques are suitable depending on the nature of the stored goods and the frequency of use. A distinction is made between the movement of load units with conveyors, the movement of load units on fixed racks, and the movement of load units with moving racks. The load units in the channel rack warehouse can be moved within the channel. In push-in channels, the load units are stored and retrieved from one side. In flow channels, on the other hand, the units are stored and retrieved from opposite directions.
An active flow rack warehouse with roller conveyors or a compact rack warehouse are examples of channel rack warehouses. If storage for longer periods is planned, channel rack warehouses are generally less suitable. However, a compact warehouse with satellite vehicles would be one option. If the warehouse is intended more as a short-term buffer and for transport preparation, and if there are also high article stocks, then the use of a flow rack warehouse, for example, is suitable.
Advantages and disadvantages of channel rack warehouses
The advantages of channel rack warehouses are:
- High space utilization
- Good degree of automation
The disadvantage is that loading units are sometimes difficult to access when they are arranged in narrow channels close to each other. This poor accessibility can in turn lead to long access times. In addition, the use of channel capacities is limited by the limited filling level when channels are filled with only one type of item. On average, the channels are less than 100% full.
Further reading
- Definition of “picking” and common picking methods
- Definition of a range of requirements for picking systems
- Allocation strategies for warehouse and picking systems
Back to TUP
