Insulated packaging maintaining the cold chain in the supply chain
Insulated packaging is used for products that are sensitive to temperature and environmental influences (see temperature-controlled logistics). In general, they ensure that the cold chain is maintained throughout the supply and value chain.
Insulated packaging: active and passive cold chain
Food, and increasingly medical and chemical products, depend on their intact and hygienic condition being maintained during transport between manufacturer, wholesaler, retailer and consumer; this condition is primarily dependent on the optimum temperature. While an active cold chain involves the continuous cooling, temperature control and recording of inventories, with the vehicles and warehouses used for this purpose being equipped with cooling technology, a passive cold chain relies on insulated packaging to keep the temperature within a certain range; temperature monitoring is not necessarily required, although it can be supported by additional measures such as dry ice. Passive cooling is usually an intermediate stage in the cold chain, generally on the way to the end consumer. Insulated packaging is also increasingly used in this context, and new solutions in terms of materials and methods are constantly being developed, also with a view to contemporary environmental compatibility.
Insulation techniques and temperature control
Depending on the inventory, duration, region and season, transportation with passive cooling can be carried out only occasionally, seasonally or even year-round. Since actively cooled transportation incurs significantly higher costs, transportation service providers often decide on a day-to-day or weather-dependent basis whether passive cooling is appropriate. In the conventional approach, special packaging (insulated packaging) is used in combination with passive cooling using dry ice.
The increasing use of insulated packaging is closely linked to the constantly growing number of products that require refrigeration. This increase is mainly due to developments in the pharmaceutical, cosmetics and food industries. GPS-based fleet management systems are being used more and more to ensure that temperature ranges are maintained. This makes it possible to permanently record and check the cooling temperature so that quick action can be taken in the event of deviations. Since legislators are prescribing more and more regulations and values, particularly for pharmaceuticals, many affected companies now require a cold chain management system that deals with the control and organization of the cold chain, both in logistics and in production.
Technical systems / providers for temperature control
- Fresh Check
- The blue point from BASF / Freshpoint (Israel)
- 3M / USA
- The CheckPoint label from Vitsab
- Plastic chip PolyTakSys / University of Tel Aviv
In this context, radio frequency identification (RFID) is proving to be a key technology. RFID can be used to ensure control and documentation quality even where conventional systems reach their limits and suffer from a lack of data accuracy and transparency. For example, each individual package can be equipped with a reusable RFID chip that measures the exact temperature directly at the inventory (see temperature-controlled logistics).
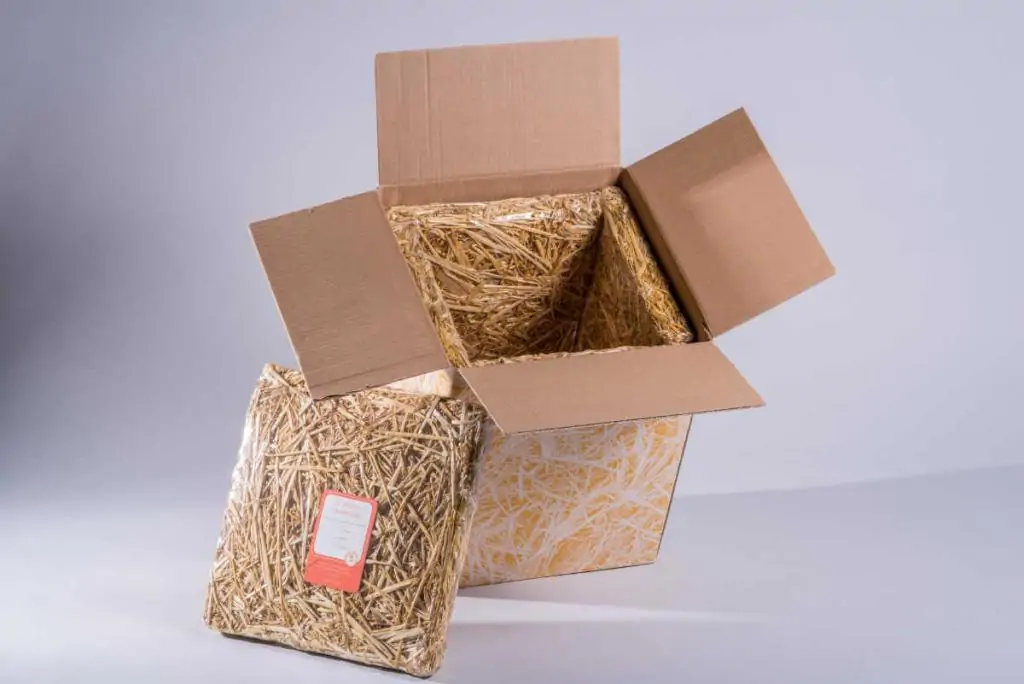

Landpack: cushioning and insulating material made from straw.
Insulated packaging and the environment
Conventional insulated packaging consists of or contains materials such as polystyrene, which is known to be non-biodegradable and therefore not environmentally friendly. New solutions are constantly being developed to replace conventional materials and methods, particularly from an ecological point of view. These materials include hemp and straw, which are increasingly being used in particular for the transport to the end consumer, i.e. the last part of the cold chain.
“In our opinion, grocery stores will suffer the same fate as the rest of the retail sector. Soon it will be perfectly normal to have your groceries delivered to your doorstep. Why carry them? In 2013, however, there was not a single ecological alternative to polystyrene worldwide – not a single non-plastic-based insulated packaging. Shippers offered prizes if someone could just name an environmentally friendly insulating packaging. So our goal was to develop exactly that kind of packaging that everyone was looking for. It wasn’t part of the plan that our Landbox would even surpass Styrofoam in many of its properties, but fortunately that just happened.”
Patricia Eschenlohr from Landpack / Source: For Founders
On the one hand, polystyrene is based on petroleum, and on the other hand, the energy required for its production is many times higher than for insulating packaging made of hemp or straw. Since straw is available locally, transport distances during production are also minimized.
Summary: Insulated packaging
Temperature- and environmentally sensitive products require insulated packaging for transportation and to maintain the cold chain. Conventionally, polystyrene is used for this purpose, sometimes in combination with dry ice. However, environmentally friendly alternatives now exist that are made of straw or hemp, for example, and in some cases have better insulating properties than conventional materials and methods.
Image Landbox: Verpackungspreis.de/DVI German Packaging Institute
If you are interested in the supply chain, then read the articles Supply Chain Management and Complexity Costs – Additional Expenses in the Supply Chain.