In German-speaking countries, the English term “warehousing” is being used more and more often, even though it is actually synonymous with warehouse logistics, storage or stockkeeping. However, it is usually not used as a pure Anglicism for existing German expressions, but rather to refer to the transfer of warehouse logistics to an external service provider (be it 2PL, 3PL, 4PL, 5PL). So when the term warehousing is used in German, it refers to the outsourcing of warehousing.
What is being outsourced?
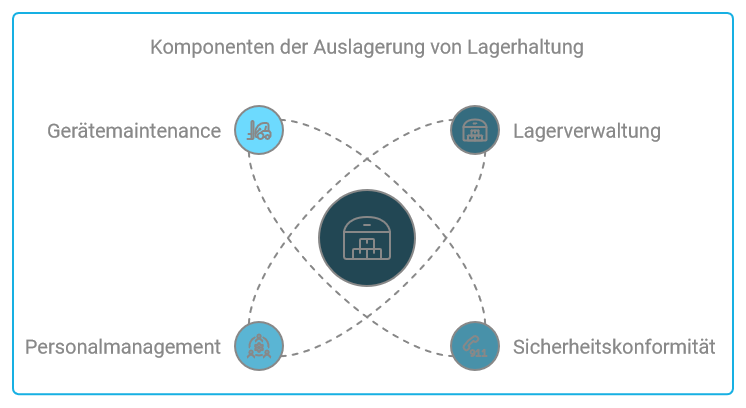
In warehousing, the external service provider not only provides storage space, but also fulfills all the functions associated with warehousing. This includes warehouse management, using appropriate software or a warehouse management system. This means that all processes in the warehouse are monitored, checked, controlled and optimized by the software; in other words, all processes from goods receipt to goods issue. In addition to the usual processes such as storage, retrieval, picking and possibly packaging, labeling and distribution, the external service provider also takes on other tasks. These include, in particular:
- Adherence to and implementation of safety measures (for example, fire protection and occupational safety) as well as the correct use of safety equipment (PPE).
- Having sufficient warehouse staff and providing them with the appropriate training.
- Maintenance of machines such as industrial trucks.
Why outsource warehousing?
Outsourcing warehousing logistics can have a variety of reasons. The cost factor always plays a role, but the question of whether it is more cost-effective to operate your own warehouse or to regularly pay a service provider for warehousing is not the only deciding factor. The following is a list of aspects that show the trade-off between in-house warehousing and third-party warehousing:
- Sometimes it is simply a question of the total costs. What is the more cost-effective solution in a given time frame and for a given set of conditions?
- There is a lack of the necessary investment capital. The investment costs for a warehouse, including machinery and personnel, are too high compared to the running costs for warehousing.
- The necessary know-how to efficiently organize your own warehousing is lacking. This is because warehouse logistics does not achieve a status quo that then has to be simply maintained. Instead, like intralogistics in general, it is subject to continuous optimization. Faster throughput times, higher process reliability and more efficient workflows, while at the same time complying with higher safety standards and permanently keeping an eye on costs, are not just a question of money, but also of expertise and experience.
- Expansion of the product range. If, for example, a company introduces a new product that cannot be stored at the already available locations due to its shape, dimensions or weight, or if raw materials and materials are needed for it that cannot be stored at the previous storage locations, then this warehousing must be transferred to an external service provider. The same applies to goods whose storage must meet certain requirements, such as cooling or the storage of hazardous materials. Thus, an expansion of the product range may necessitate warehousing.
- Opening up new markets. If markets in other regions and countries are opened up, it may not yet be worthwhile for a company to have its own warehousing or it would involve too much risk. However, only operating a central warehouse in the home region makes it more difficult to open up the new market. Accordingly, it makes sense to use warehousing in the new region and thus have a decentralized warehouse structure.
Summary
In warehousing, an external service provider takes over a company’s warehousing or warehouse logistics (2PL, 3PL, 4PL, 5PL). To this end, certain conditions are defined under which the external service provider takes care of this area of the company. Not only the rooms, i.e. storage space, but also all processes within the warehouse between incoming and outgoing goods are outsourced. Warehousing also includes other tasks such as staff training, machine maintenance and compliance with safety measures. The use of the term “warehousing” in German is to be distinguished from its meanings in English. There, warehousing refers to the terms storage, stockkeeping and warehouse logistics and not exclusively to the transfer of warehousing to an external provider. A special form of warehousing is the data warehouse, in which data is outsourced and for which there are also specialized providers.
