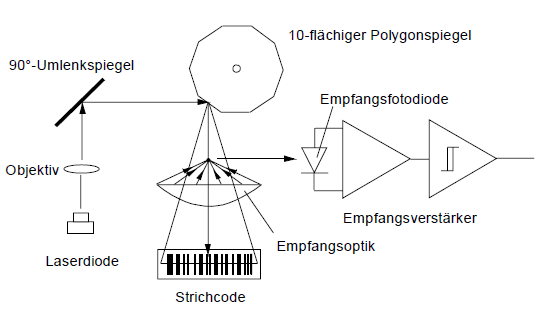
In scanners, the dynamic deflection of the laser beams is achieved by means of mirror systems. This involves an arrangement of fixed and rotating mirrors. The polygon mirror is driven by a motor and projects a moving and repeating light spot onto the code surface. Depending on the speed of rotation and the number of mirrors, scanning rates of 100-800 scans/second can be achieved.
The various reflections of the dark code bars and the light gaps are focused by the mirror-lens system onto a photoelectric receiver and converted into the corresponding electrical signals.
For more information about laser scanners, see The structure of a laser scanner.
Image source: © Benjamin Haas – Fotolia.com
