Dropshipping
Dropshipping, also known as drop shipping, describes a relationship between the online retailer and wholesaler as well as with the customer/buyer themselves. In this special type of trade, the online retailer has no contact with the goods.
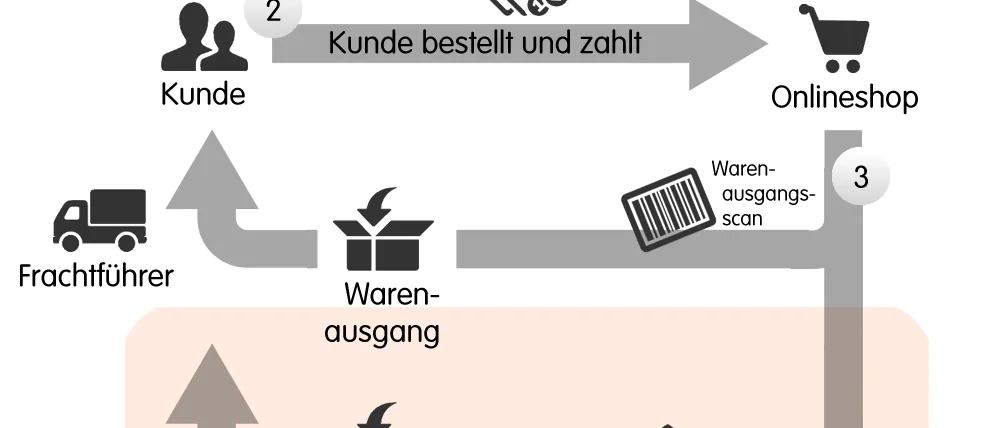
Normally, the customer orders their goods from the online store, pays the invoice and receives the ordered products directly from the online retailer. With dropshipping, however, the logistical business processes such as storage and shipping are redistributed. The customer first sends their order via an online store and pays the invoice amount to the retailer. However, the retailer does not ship the goods themselves, but has them shipped directly by the respective manufacturer or a wholesaler. The online retailer is only responsible for the store, order process and invoicing. The wholesaler or manufacturer is responsible for logistical tasks such as storage and shipping.
Special feature: Although the goods are sent directly to the customer by the wholesaler or manufacturer, only the online retailer handles the withdrawal or return. The retailer is the legal owner of the goods when they are returned.
Dropshipping processes:
- Customer: order, payment, returns
- Online retailer: store, invoicing for customers, packing order to manufacturer
- Manufacturer / wholesaler: invoice for goods and services to retailer, shipping to customer
Advantages of dropshipping:
- No own warehouse
- Goods are only paid for by the retailer when sold
- Customers are supplied automatically
- Online retailer does not have high personnel costs
- Manufacturer gets more order reach without own effort
Information on procurement logistics can be found in the article Milkrun concept.
Image rights: Volker Schukai / License: CC BY-SA 3.0