Product Lifecycle Management, or PLM for short, describes a holistic approach to bundling product information. It involves a kind of cross-company management and control of the flow of information about a product along the entire value chain. The industry speaks of collecting the information that arises in the course of a product’s life cycle. This includes, for example, information from construction, production, sales, service, dismantling and recycling.
Product Lifecycle Management is generally based on detailed product information, which is initially collected as part of product planning and production. This also includes product data that is collected and stored in a structured way outside the company, by external service providers and suppliers along the supply chain. As a rule, the management structure of PLM can be divided into three phases:
- Beginning of Life (BoL)
- Middle of Life (MoL)
- End of Life (EoL)
One of the objectives of a PLM is to provide employees with product information in high quality, including additional information (images, videos) at the right place and on request (see also PLM benefits). The three phases mentioned above include the following information interfaces:
- raw material extraction, supplier
- development (design processes), construction, production of new products; including machine and software information during production.
- Sales, collaboration with suppliers, warranty management, customer communication
- Disposal, taking products off the market (product discontinuation), recycling
Important: PLM doesn’t just use information about the respective product. It also takes into account and includes people and their expertise who are relevant to solving specific product issues. This also includes process-related improvements and past success stories that improve overall business productivity. A kind of social network within the company.
Product Lifecycle Management is the product-related and cross-company information management. PLM includes the planning, control and organization of the processes required for the generation and holistic management of all data, documents and resources throughout the entire product lifecycle.
Technical University of Kaiserslautern, Chair of Virtual Product Development
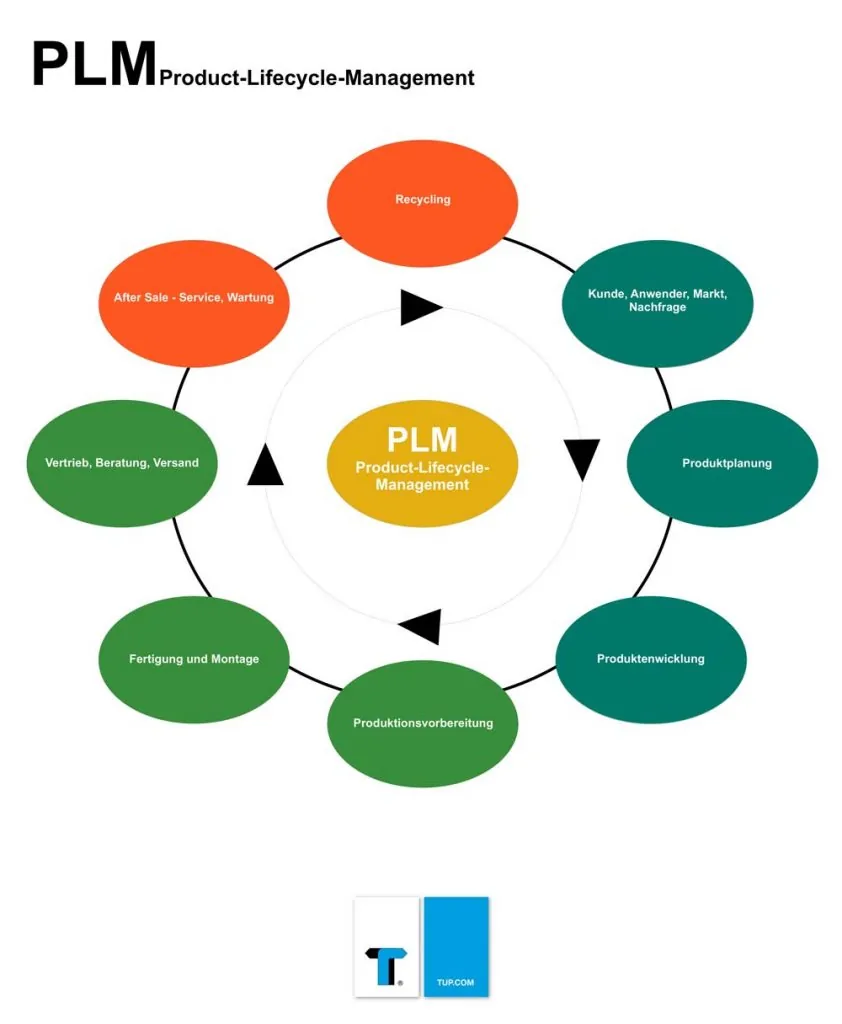
The PLM is divided into the main topics shown here: design, construction, production, services (please click on the image to enlarge).
The advantages of product lifecycle management (PLM)
- Planning and production become transparent.
- New standards are created.
- The product is completely transparent.
- Strengthening of competitiveness.
- All employees involved are on the same level of knowledge.
- Productivity through repeatable and successful processes.
Important: PLM is usually a software-based information system that is characterized by a so-called coherent data structure. In other words, the information is not only coherent; the systems involved also act in a consolidating manner. In addition to the classic product information, suitable interfaces ensure that the relevant information from the producing and transporting peripherals is available.
Companies often rely on a so-called ‘Product Data Management’ (PDM) for the implementation of a Product Lifecycle Management. This is a software that specifies how product data (documents) and product information are stored and managed. Another example of such software is the Product Information System – PIM for short.
For more information on this topic, see also Supply Chain Management and ‘What is Supply Chain Management?
Teaser image: Max Pixel
